Gitlab Workflow
- 参考
策略配置
label 策略
created labels for “discussion”, “backend”, “frontend”, “working on”, “staging”, “ready”, “docs”, “marketing”, and “production”
工作流
功能开发的工作流
- 创建一个feature issue,打上 “discussion”
- 讨论通过,删除 “discussion” 标签 ,打上 “working on”,指派给开发人员。
- 开发人员创建 feature-branch ,开发完成,创建 MR(Merge Request)申请将 commit 提交到 feature-branch 上。
- MR 描述包含 issue closing pattern ,例如:Closes #xxx
- 其他团队成员,对 MR 进行 review,测试是否能编译通过,测试功能。
- 测试通过后,feature issue 删除 “working on” 标签 ,打上 “staging” 标签。
- 线上验收通过后,从 “staging” 标签 改为 “ready”。
- 文档人员将 标签改为 “docs”,编写文档。
- 文档写完,运维人员将功能上线,标签改为 “production” ,关闭 issue。
版本管理策略
Git Flow
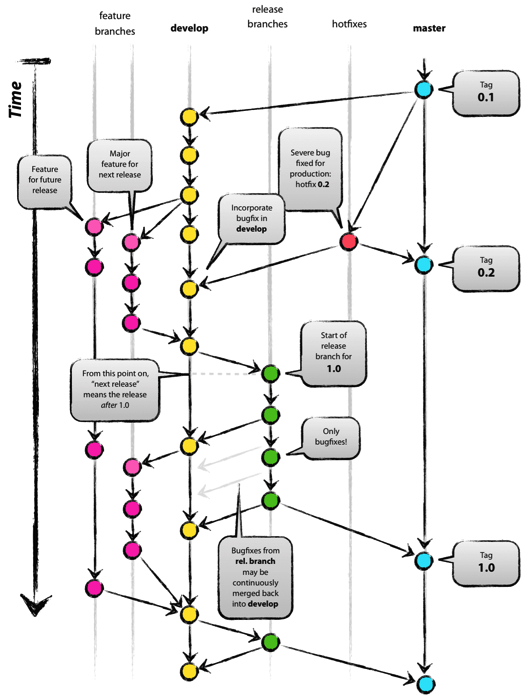
- 存在问题
- developers must use the develop branch and not master, master is reserved for code that is released to production.
- the complexity introduced by the hotfix and release branches.
- too complex for most of the use cases. doing releases doesn’t automatically mean also doing hotfixes.
Gitllab Flow
- has only feature branches and a master branch.
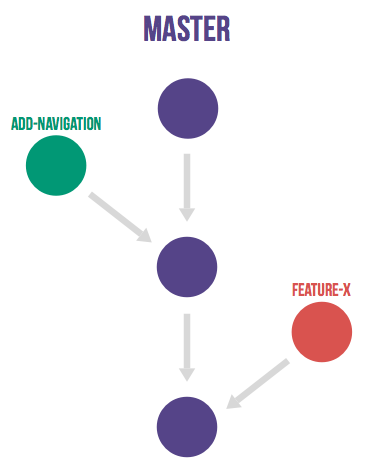
Prodcution Branch with Gitlab Flow
- 需要发布时,才从 master 合并到 production-branch
- 利用 production-branch 部署
- 通过 production-branch,可以统计开发时间
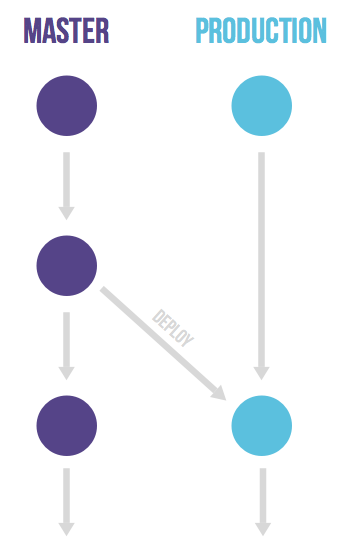
Release branches with GitLab flow
- bug fixes are first merged into master and then cherry-picked into the release branch.
- This is called an ‘upstream first’ policy that is also practiced by Google and Red Hat.
- Every time a bug-fix is included in a release branch the patch version is raised (to comply with Semantic Versioning) by setting a new tag.
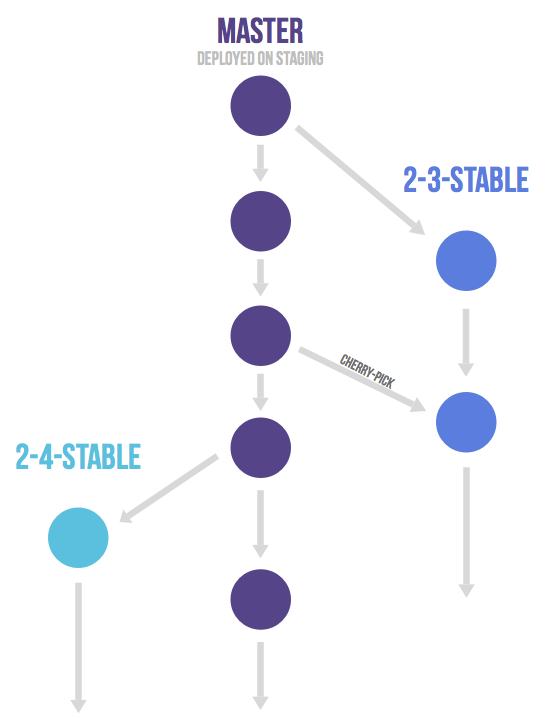
Merge/pull requests with GitLab flow
- 创建 MR,但不指派任何人,在描述或者备注中 cc 给相关的开发人员(如,/cc @mark @susan)
这个做法表示,还没准备好发布,但是欢迎大家反馈问题。其他人可以查看、备注,甚至提交修改。 - 如果 MR 准备好了,就指派给 管理员 (someone with master authorizations) review 吧;管理员不爽这个MR,是可以直接丢弃掉的,不会 Merge 到主干上。
- 每次 MR 被 merge 到主干,采用的是 non fast forward 模式( –no-ff ),一定会产生一个commit。
Issues with GitLab flow
- Having a reason for every code change is important
- keep the scope of a feature branch small
- In GitLab each change to the codebase starts with an issue in the issue tracking system.
- 处理 issue 前先从 master 开一个分支,分支名称以issue 号开头,如, ‘15-require-a-password-to-change-it’.
- 开发完成或者想与 team 讨论 issue,创建一个 MR。对于要讨论的 MR,标题冠以 WIP,意为 work-in-process
在 MR 中关闭或者链接 Issue
- commit messages 包含 fixes #14, closes #67, 等内容,或 MR 描述包含这些内容,MR 被 merge 进主干时, issue 被自动关闭。
- 也可以使用 #xxx ,来仅仅关联 commit 和 issue。
Issue closing pattern
默认可以使用的关键字,在 commmit message 中使用,可自动关闭 issue
- Close, Closes, Closed, Closing, close, closes, closed, closing
- Fix, Fixes, Fixed, Fixing, fix, fixes, fixed, fixing
- Resolve, Resolves, Resolved, Resolving, resolve, resolves, resolved, resolving
例子:
1 2 3 4 5 | Awesome commit message Fix #20, Fixes #21 and Closes group/otherproject#22. This commit is also related to #17 and fixes #18, #19 and https://gitlab.example.com/group/otherproject/issues/23. |
附录
产品开发生命周期
“going faster from idea to production in 10 steps.”
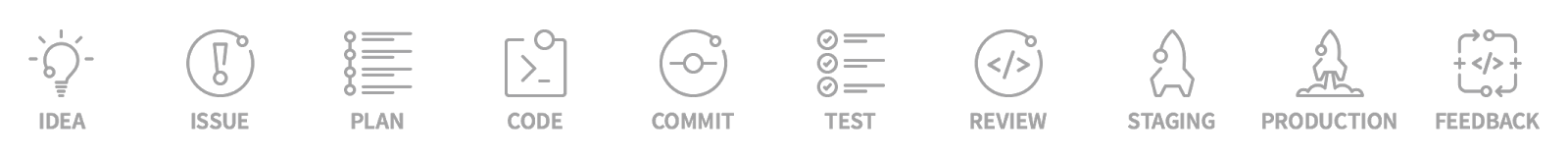
- IDEA: 集成了 Mattermost.
- ISSUE: 自带 Gitlab Issue Tracker.
- PLAN: 自带 GiLab Issue Board.
- CODE:
- COMMIT:
- TEST: 集成了 GitLab CI
- REVIEW: 自带 Gitlab Code Reviewed
- STAGING:
- PRODUCTION:
- FEEDBACK: 集成了 Cycle Analytics